|
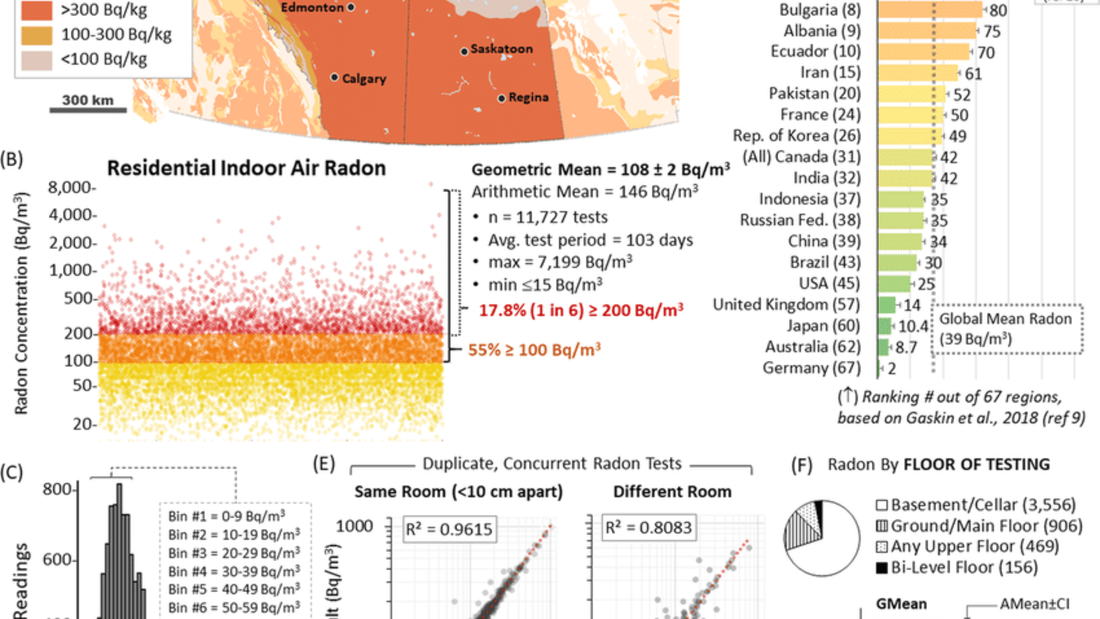
Radon gas exposure is becoming more of a worry in modern homes across North America, bringing major health dangers such as an increased risk of lung cancer. Recent research has highlighted the worrisome trend of rising radon levels, particularly in the North American Prairie region. This raises the question, "Does radon rise differently in various geographical areas?" Understanding how radon behaves and moves within homes is crucial for assessing the potential risks it poses to occupants. Therefore, the importance of radon testing cannot be overstated, as it allows homeowners to promptly identify and address high radon levels, ensuring a safer living environment for their families. This article aims to comprehensively understand the factors contributing to this growing problem, including the impact of building design, occupant behavior, and seasonal variations. Read on to learn more. Radon Exposure in the North American Prairie Region
Factors Influencing Radon Exposure in Modern HomesImpact of Year of Construction
Building Characteristics
Occupant Behavior
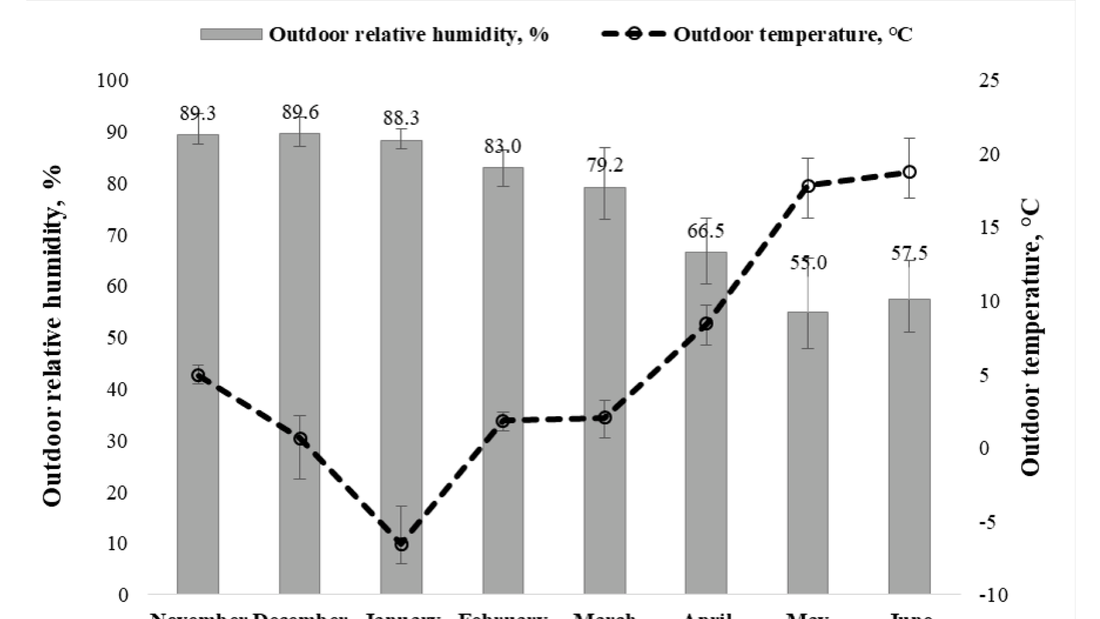
Seasonal Variations in Radon Exposure
Public Health Implications and Recommendations
Recommendations for Stakeholders
ConclusionThe rise in radon exposure within modern North American homes, particularly in the North American Prairie region, demands urgent attention. Understanding the risk factors associated with high radon levels, the influence of building design, occupant behavior, and seasonal variations is essential in formulating effective prevention strategies. By raising awareness and implementing measures to mitigate radon exposure, we can safeguard the health and well-being of individuals and families. Policymakers, builders, and homeowners must work together to address this significant public health concern and prioritize radon testing and mitigation. We can only effectively combat the growing radon exposure in modern homes through collective efforts. FAQsWhat is radon gas, and why is it a concern in homes?Radon gas, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, is produced by the decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water. It can enter homes through foundation faults and floor and wall gaps. Long-term radon exposure raises the risk of lung cancer, which is cause for concern. How does the year of construction influence radon levels in homes?Newer homes tend to have higher radon levels compared to older structures. This is likely due to changes in building practices and materials used in modern construction, which may unintentionally allow greater radon penetration. What factors in building design contribute to increased radon exposure?Several building characteristics can influence radon levels. These include larger surface areas, taller ceilings, fewer storeys, specific foundation types (e.g., basements), and curtain wall construction materials. These factors can create more opportunities for radon entry into the living spaces of a home. How does occupant behavior affect radon exposure?Occupant behavior, such as thermostat settings and window opening habits, can impact the air dynamics within a home. While there is no significant correlation between thermostat settings and radon levels, reduced window opening behavior, especially on upper floors, has been associated with higher radon concentrations. Do radon levels vary seasonally?Contrary to popular belief, the research has shown that radon levels do not significantly fluctuate between seasons. Nearly half of the residences displayed minimal differences in radon levels between winter and summer, challenging the notion that radon levels are highest during winter. What are the public health implications of radon exposure?Radon exposure is a significant public health concern due to its link to lung cancer. Long-term radon exposure can raise the chance of getting lung cancer, making it critical to take proactive steps to limit radon exposure in the household.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorIndianapolis Radon Mitigation: Trusted experts in radon mitigation, committed to providing efficient and effective radon system installations to ensure the safety and well-being of your home and family ArchivesCategories |
|
SERVING INDIANAPOLIS & SURROUNDING AREAS
|
BUSINESS HOURS
Mon-Fri: 7am-7pm Sat & Sun: 9am-5pm OUR SERVICES Radon Mitigation Radon Testing Radon System Installation Indianapolis Radon Mitigation 5341 Waterton Lakes Dr, Indianapolis IN 46237 317-203-8117 |
Call Today!
317-203-8117 CREDENTIALS
In Business Since: 1988 Memberships & Affiliations NRPP national radon proficiency program State Licensing License #: RMT00798 |